Organizations can use the following checklist to gather information that is used to configure Outposts:
| Parameter | Description |
| Number of CNDs | Two recommended |
| Organization ASN | Existing organization BGP ASN |
| Number of uplinks | Number of uplinks between each CND and OND (1, 2, 4, 6, or 8 recommended) |
| Uplink speed | 1 Gbps, 10 Gbps, 40 Gbps, or 100 Gbps |
| Fiber type | SingleMode Fiber (SMF) or Multi-Mode Fiber (MMF) |
| Optical standard | LX, SX, IR, SR, LR, IR4, LR4, ESR4, SR4, MSA, CWDM4 |
| Service link VLAN | Any VLAN between 1 and 4094 |
| LGW VLAN | Any VLAN between 1 and 4094 |
| LACP LAG 1 | Uplinks between Outposts Network Device 1 and Customer Network Device 1 |
| LACP LAG 1 | Uplinks between Outposts Network Device 2 and Customer Network Device 2 |
| Service link BGP subnet 1 | /30 or /31 Subnet 1 |
| Service link BGP subnet 2 | /30 or /31 Subnet 3 |
| LGW BGP subnet 1 | /30 or /31 Subnet 2 |
| LGW BGP subnet 2 | /30 or /31 Subnet 4 |
| Service link ASN | Private ASN for service link |
| LGW ASN | Private ASN for LGW |
| Service link infra subnet | A CIDR (/26 required, advertised as two contiguous /27 subnets). |
| Private connectivity subnet | A subnet created in the AWS Region that acts as an AWS Outposts service link anchor |
Table 10.6 – Network readiness checklist
AWS Outposts connectivity to AWS Region
VMC on AWS Outposts requires a persistent connection to a nearby AWS Region designated as the home region. A service link connection is set up between the Outposts rack and the home region for management and control plane traffic. The service link can also be used for data plane traffic between AWS Outposts and AWS Region workloads. Continuous service link connectivity with a minimum bandwidth of 500 Mbps (1 Gbps is recommended) is required, which can be established using either of the following options:
- Public connectivity to the AWS Region:
- Via the internet on-premises
- Via the internet using an AWS Direct Connect Public Virtual Interface (VIF)
- Private connectivity to the AWS Region:
- Using an AWS Direct Connect private VIF
Public connectivity
VMC on AWS Outposts public service link connectivity is established using an internet connection at the on-premises organization location. The AWS Outposts rack connects to service link public endpoint IPs using a group of encrypted tunnels using Transport Layer Security (TLS). The following diagram shows VMC on AWS Outposts establishing a service link using the public connectivity model.
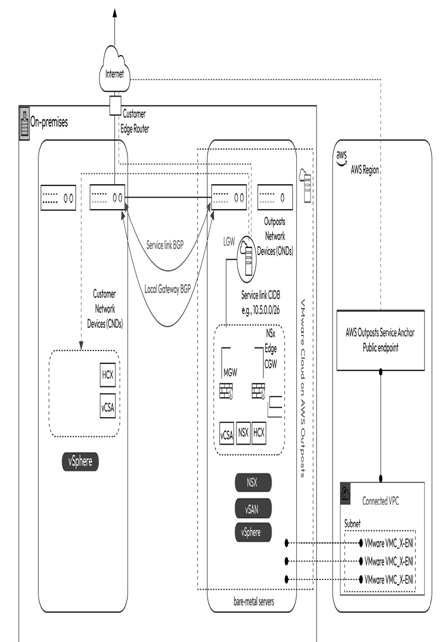
Figure 10.11 – VMware Cloud on AWS Outposts service link public connectivity
Figure 10.11 depicts VMware Cloud on AWS Outposts installed on-premises at the organization, with a service link established over the internet to the AWS Outposts service anchor point public endpoint in the AWS Region. It is critical to have reliable underlying service link connectivity to the AWS Region to ensure that VMC on AWS Outposts remains operational. Therefore, organizations should ensure the availability of resilient and reliable internet connectivity that Outposts can leverage.
For enhanced security, organizations must allow outbound connections from Outposts toward the AWS Region so that the service link tunnel can only initiate connections from Outposts to the Region, as indicated in the following table:
| Protocol | Source Port | Source Address | Destination Port | Destination Address |
| UDP | 443 | Outposts service link /26 | 443 | AWS Region’s (homed to Outposts) public routes |
| TCP | 1025-65535 | Outposts service link /26 | 443 | AWS Region’s (homed to Outposts) public routes |
Table 10.7 – Prerequisite firewall rules for public connectivity
