Amazon EFS is a scalable file storage solution that can grow from gigabytes to petabytes of data without pre-provisioning storage or managing storage capacity and performance. EFS supports full filesystem access semantics, including strong consistency and file locking. In addition, Amazon EC2 instances and VMware VMs can access an EFS filesystem simultaneously. Figure 8.5 illustrates the integration of VMware Cloud on AWS workloads with Amazon EFS using a VPC gateway endpoint.
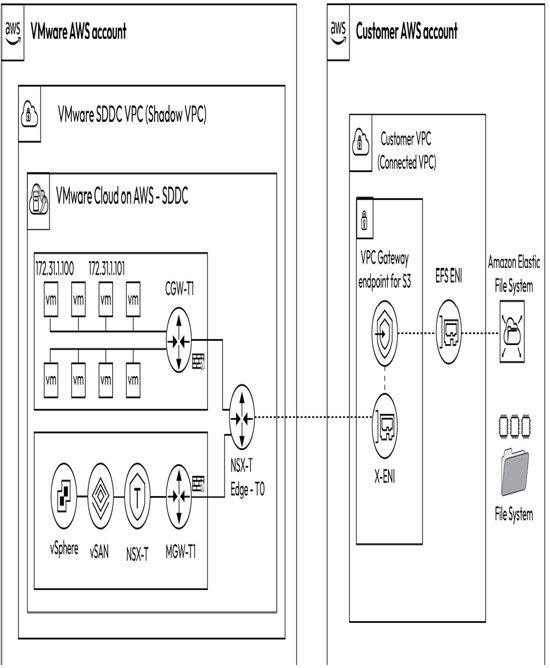
Figure 8.5 – Amazon EFS integration with VMware Cloud on AWS
Workloads running on VMware Cloud on AWS SDDC can utilize an EFS VPC interface endpoint to access EFS filesystems residing in the connected VPC via the NSX Edge Tier-0 Logical Router and X-ENI. Multi-Availability Zone (AZ) filesystems have ENIs associated with each AWS AZ, enhancing availability and resiliency. Amazon EFS supports a wide range of workloads and applications, including big data and analytics, media processing workflows, and content management. Furthermore, EFS can be utilized as secondary storage to offload VM data from the primary vSAN storage.
Integrating Amazon FSx for Windows File Server
Amazon FSx for Windows File Server is a scalable file storage solution accessible through the Service Message Block (SMB) protocol built on Windows Server. Amazon FSx provides high throughput and IOPS with consistent sub-millisecond latencies. In addition, an FSx filesystem can be accessed simultaneously by Amazon EC2 instances and VMware VMs. Amazon FSx offers various administrative features, including user quotas, end user file restores, and Microsoft Active Directory (AD) integration. Figure 8.6 illustrates the integration of VMware Cloud on AWS workloads with Amazon FSx for Windows File Server and AWS Directory Service, which enables file sharing across multiple VMs.
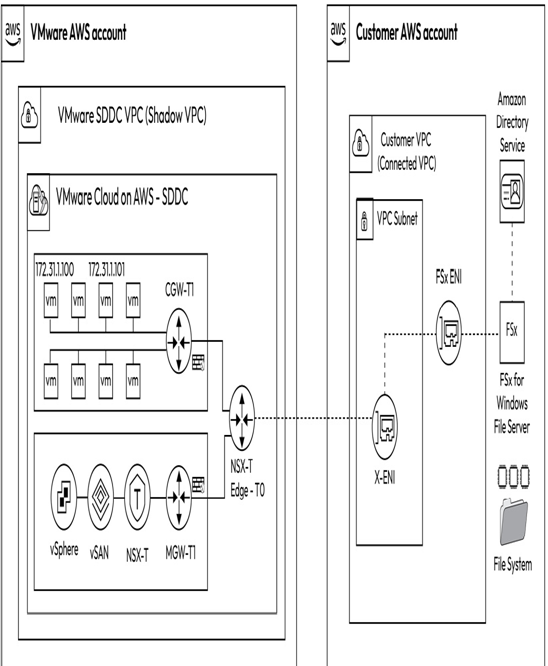
Figure 8.6 – Amazon FSx for Windows File Server integration with VMware Cloud on AWS
Workloads running on VMware Cloud on AWS SDDCs can access an Amazon FSx filesystem in the connected VPC via the NSX Edge Tier-0 Logical Router using the X-ENI. For multi-AZ filesystems, each AWS AZ where the Amazon FSx filesystem is created has a corresponding ENI created within the same AZ to enhance availability and resiliency.
VMs running on VMware Cloud on AWS SDDCs can offload data to Amazon FSx for Windows Server filesystems. The FSx filesystems act as secondary storage to complement primary vSAN storage. A diverse range of use cases that necessitate Windows shared file storage, such as CRM, ERP, custom or .NET applications, and Microsoft SQL Server, can be accommodated by using Amazon EFS for VMware Cloud on AWS SDDC workloads.
To support high availability, security, and scalability, AWS provides a range of fully managed, purpose-built database services, including relational, key-value, in-memory, document, wide-column, graph, time-series, and ledger databases. Among these, Amazon Relational Database Service (RDS) is a well-known option, enabling organizations to choose from seven popular engines, including Amazon Aurora with MySQL compatibility, Amazon Aurora with PostgreSQL compatibility, MySQL, MariaDB, PostgreSQL, Oracle, and SQL Server. Additionally, Amazon Redshift is a fully managed data warehouse tool that can effectively handle petabyte-scale data analysis.
Amazon QuickSight is a business analytics service that enables users to create visualizations, perform ad hoc analyses, and gain quick insights into their data from any device and at any time. With QuickSight, organizations can expand their business analytics capabilities to a large number of users thanks to its responsive query performance. It provides easy access to data from various sources, such as CSV and Excel files, on-premises databases such as SQL, MySQL, and PostgreSQL, and SaaS applications such as Salesforce, Amazon Redshift, Amazon RDS, Amazon Athena, and Amazon S3.
Athena is an analytics service that allows for interactive querying, utilizing open source frameworks and supporting open table and file formats. With Athena, users can easily build applications or analyze large volumes of data from over 25 different sources, including cloud systems, on-premises data sources, and Amazon S3 data lakes, using either SQL or Python.
AWS Glue is a serverless data integration service that simplifies the process of discovering, preparing, moving, and integrating data from over 70 diverse data sources and managing data in a centralized data catalog. It can be used for analytics, machine learning, and application development. AWS Glue enables organizations to create, run visually, and monitor extract, transform, and load (ETL) pipelines to load data into their data lakes. Figure 8.7 illustrates the integration of VMware Cloud on AWS workloads with Amazon RDS (databases) and various AWS analytics services, including Amazon QuickSight, AWS Glue, and Amazon Athena, along with data warehousing using Amazon Redshift.
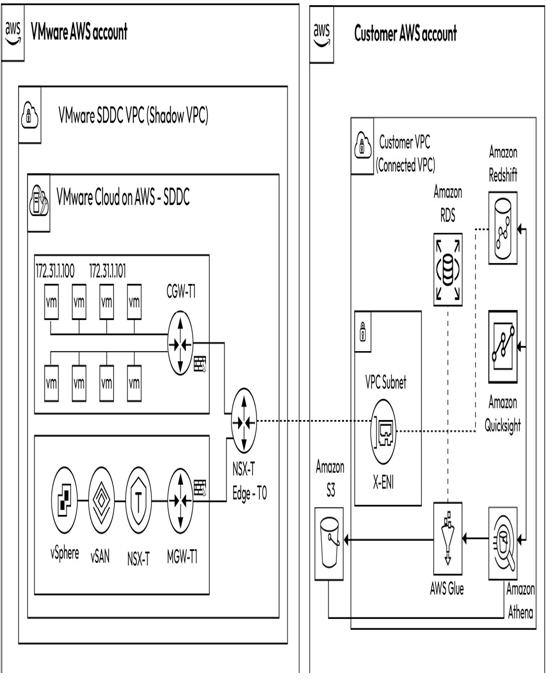
Figure 8.7 – Amazon RDS integration with VMware Cloud on AWS
As seen in Figure 8.7, workloads in the VMware Cloud on AWS SDDC have access to Amazon databases such as Amazon RDS and Redshift running in the connected VPC. Organizations can avoid managing complex database servers using Amazon’s fully managed databases. The web and application tiers can continue to run on the VMware Cloud on AWS SDDC, while the database tier can be migrated to one of the AWS-managed databases. The traffic between the web tier and app tier in the SDDC is routed through the T1 compute gateway, the T0-NSX-Edge, and over the X-ENI and eventually reaches the database endpoint.
A common use case for organizations is reducing the TCO of storage-heavy or memory-intensive on-premises databases using a purpose-built database such as Amazon RDS. Amazon RDS lets you migrate on-premises relational databases to the cloud and integrate them with VMware Cloud on AWS SDDC VMs. Amazon RDS also reduces the operational overhead organizations may incur with managing availability, scalability, and Disaster Recovery (DR) tasks.
Organizations can benefit from the proximity of data residing in the VMware Cloud on AWS SDDC and gain meaningful insights from their business data by utilizing AWS analytics service integrations. For instance, Amazon Redshift can be used to create a data warehouse that enables running analytics at scale on relational data from transactional systems, operational databases, and line-of-business applications running within the VMware Cloud on AWS SDDC.
